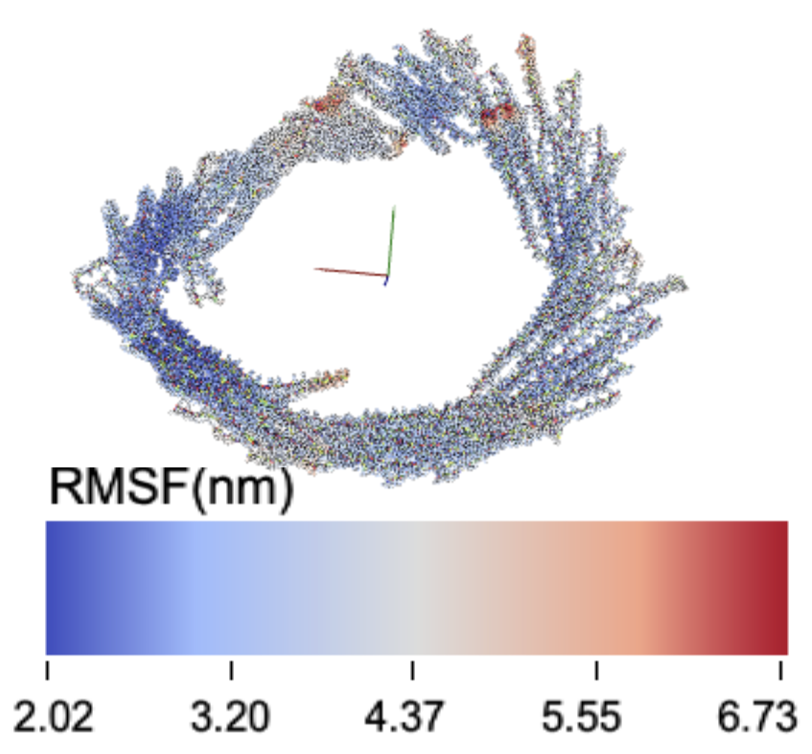
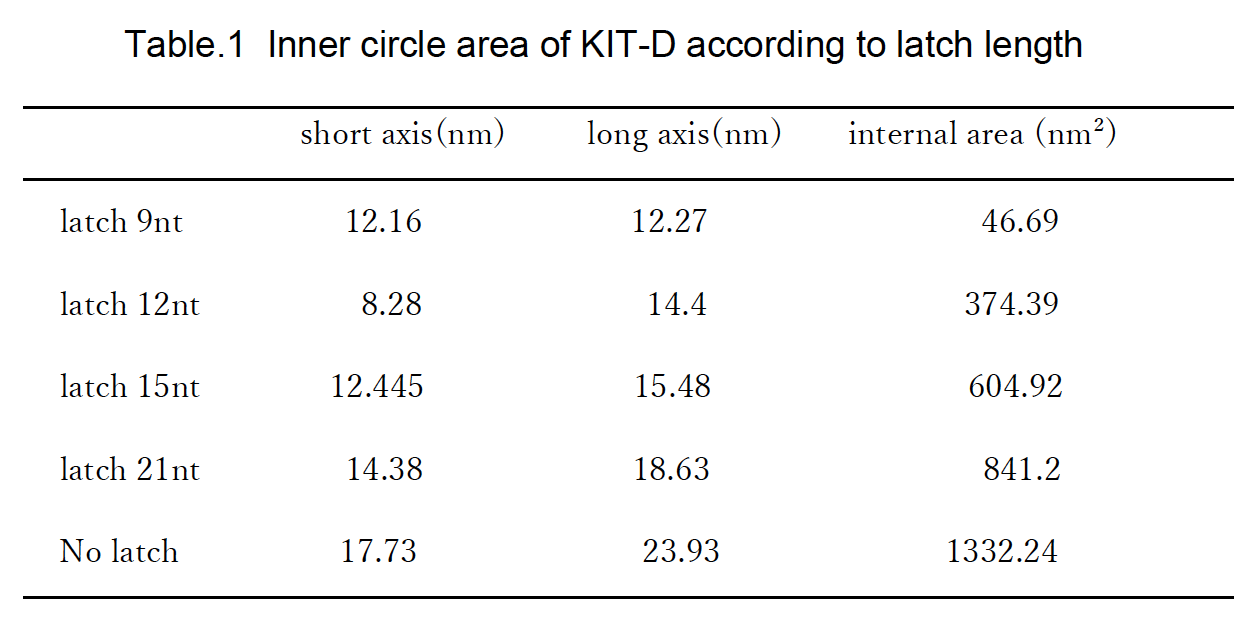
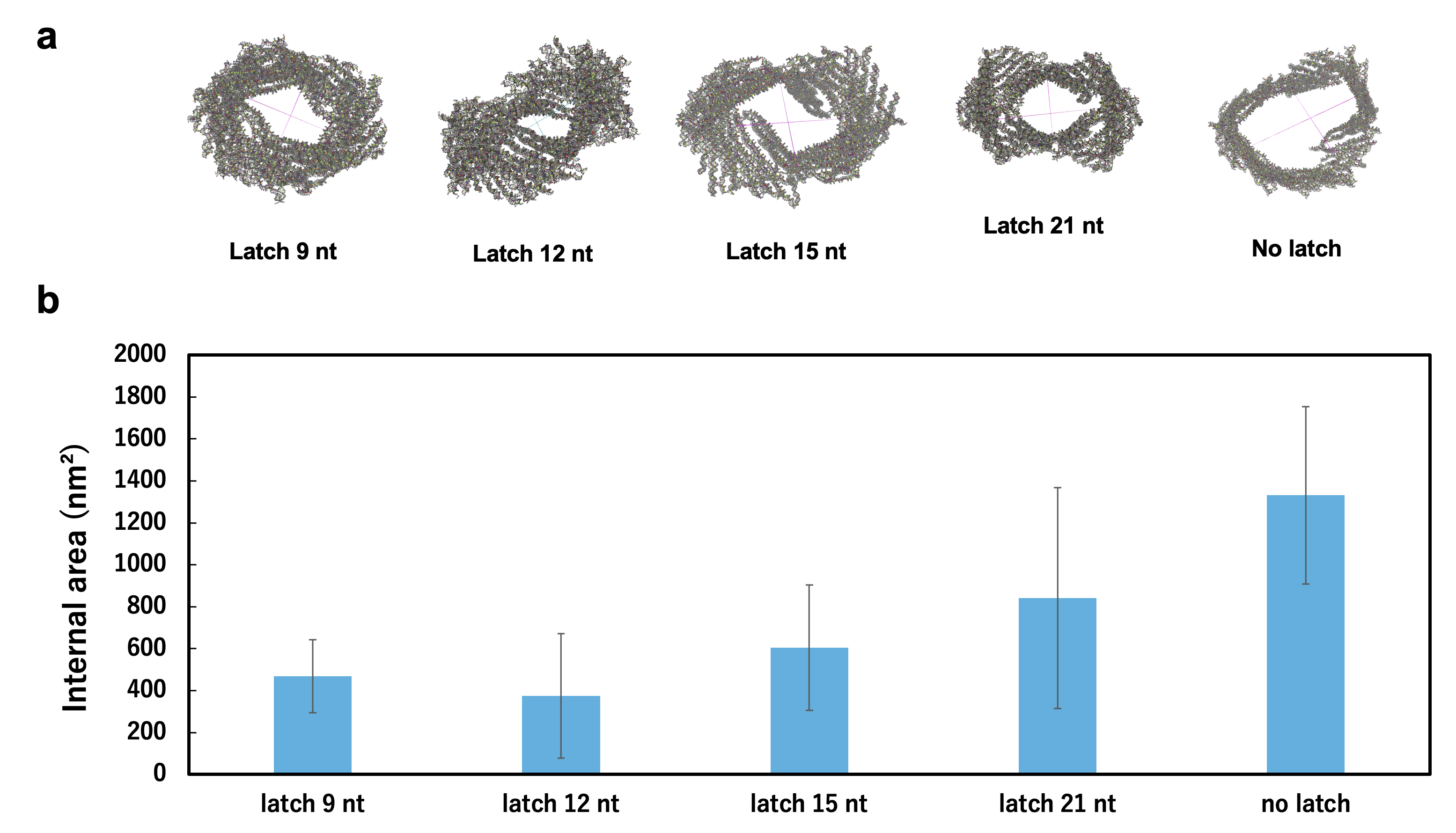
Determining the aspect of the structure
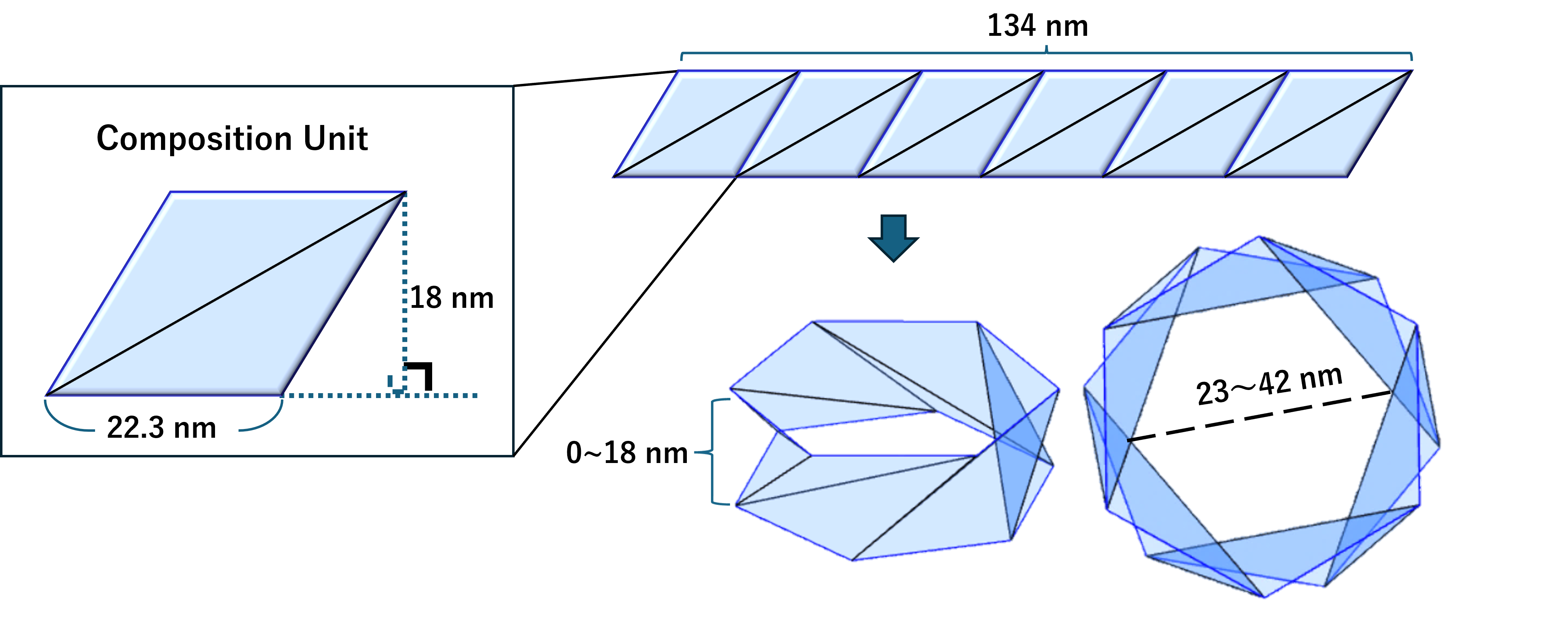
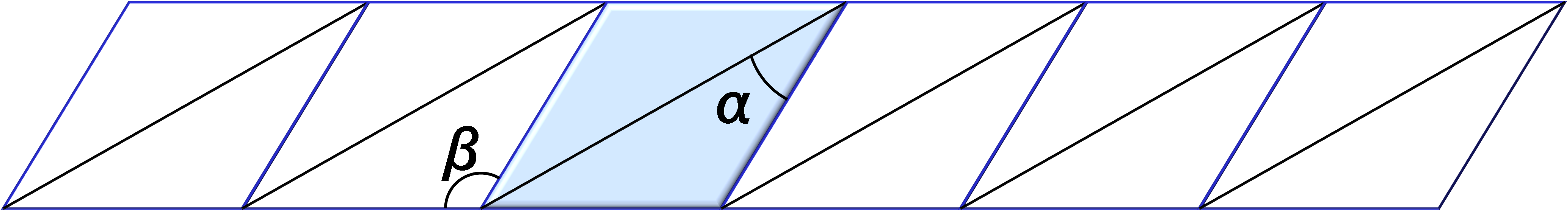
Figure 1. The basic dimensions of KIT-D
This figure shows the dimensions of the KIT-D structure. It is made
of a series of six parallelograms composed of two isoceles triangles
which are placed back to back. The parallelogram unit can be rolled
up into a tubular structure with height ranging from nearly 0 to 18
nm, and its inner diameter changing from 23 to 42 nm.
Two-layered structure to enhance rigidity
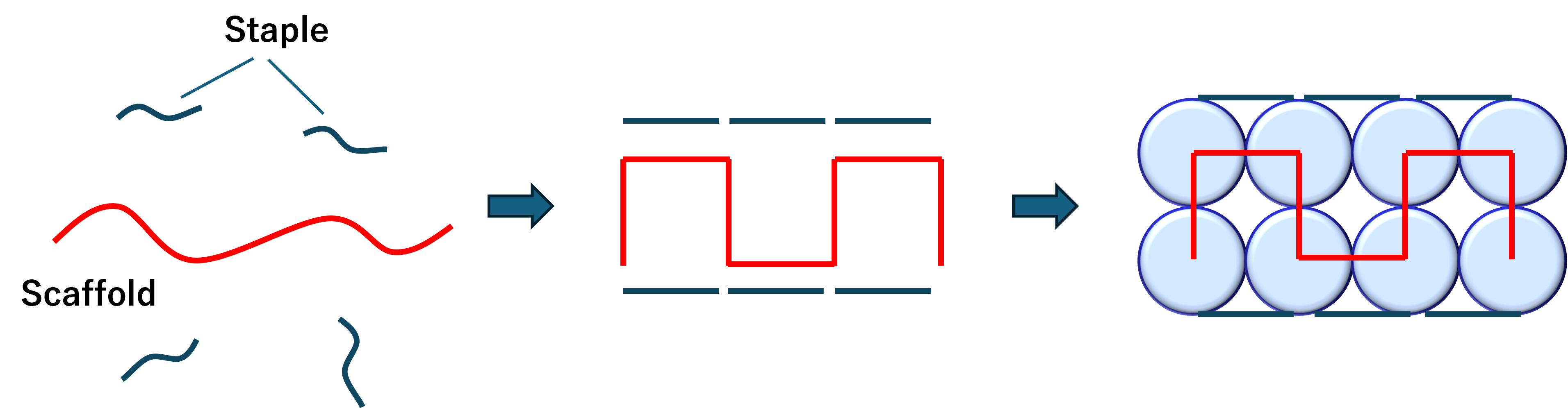
Figure 3. Formation of the two-layered structure
Staple strands were designed to fix the scaffold strand in a
meandering way to form two layers, providing durability to the
structure.
Adjusting the length and position of the hinges
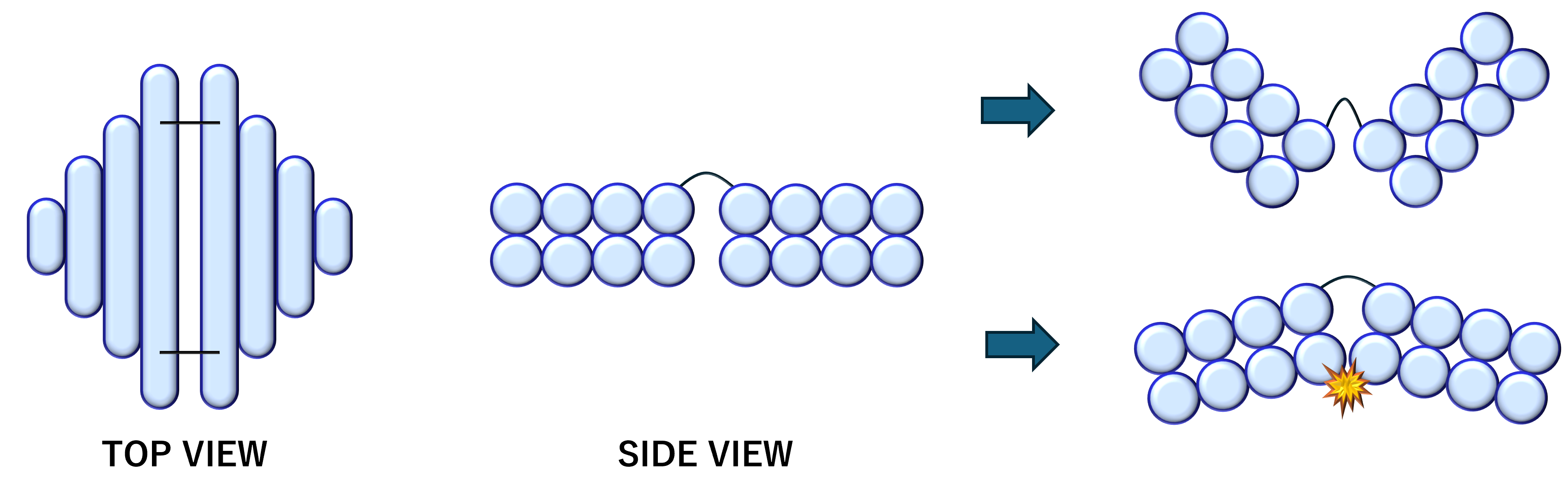
Figure 4. Positioning of the hinges to guide folding direction
Hinges were located on one side of the layer to navigate the
direction of the folding, enabling the implementation of mountain
and valley folds in desired positions.
Structural Design for Transformation
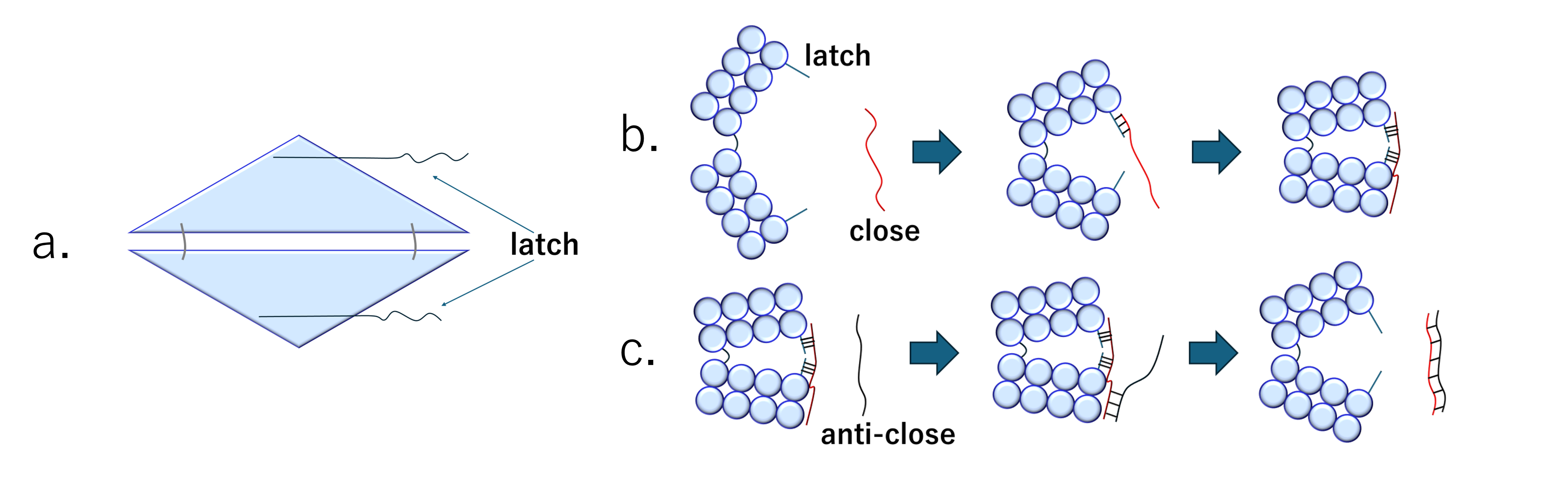
Figure 5. Positioning of latches and transforming mechanism
5a. shows that the latches are located at the tips of the
triangles.
5b. illustrates how KIT-D closes when an additional strand “close”
is added.
5c. shows the transformation of the structure to its open state when
”anti-close” is added.